Radon Mitigation
What is Radon Mitigation?
Radon mitigation involves the implementation of measures to reduce elevated levels of radon gas in indoor spaces, particularly homes and buildings. The goal of mitigation is to decrease radon concentrations to levels that are considered acceptable, typically below the recommended reference level of 4 picocuries per liter (pCi/L) or 150 becquerels per cubic meter (Bq/m³).
Radon Mitigation for Air
Typically a radon system can be installed in less than a day at a cost similar to less than most common home repairs.
The most widely accepted and commonly used method for reducing radon in homes is the installation of an Active Soil Depressurization (ASD) system. An ASD System installed in the home acts similarly to a vacuum cleaner, pulling the radon from beneath the home and venting it safely above the roofline. When installing an ASD system, a radon professional will:
- Seal all cracks including covering dirt crawlspaces if necessary.
- Drill one or more draw or suction points through the slab or crawlspace membrane deep enough into the soil blow to provide the ability to depressurize the home.
- Vent by installing a PVC pipe from the draw point up through the interior or on the exterior of the home to above the roof.
- Activate with a radon fan attached to a dedicated electric circuit.
- Monitor with a U-tube Manometer and a Radon System Alarm so the homeowner can see if the radon mitigation system is operating.
- Retest the radon level within 30 days to ensure that the radon level is reduced. The EPA recommends testing every 2 years as conditions can change over time.
- A Certified Professional will be able to evaluate your home and determine the best mitigation system for you.
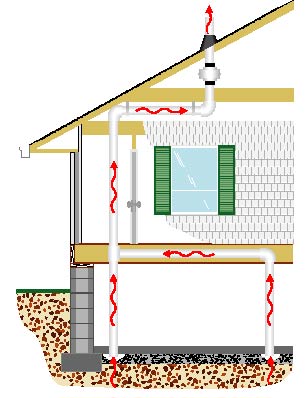
Indoor Radon Mitigation System
An indoor or interior radon system is typically installed during new construction or major renovations. PVC vent pipe is usually routed through closets or other unexposed areas to the radon fan in the attic and then through the roof to discharge the radon gas safely above the roof.

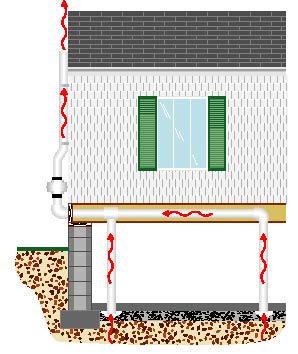
Outdoor Radon Mitigation System
An outdoor or exterior radon mitigation system is often installed in an existing home. PVC vent pipe is connected to penetration(s) in the crawlspace or basement, routed to the exterior of the home, attached to the radon fan, and run up the outside wall of the house to discharge the radon gas safely above the roof.

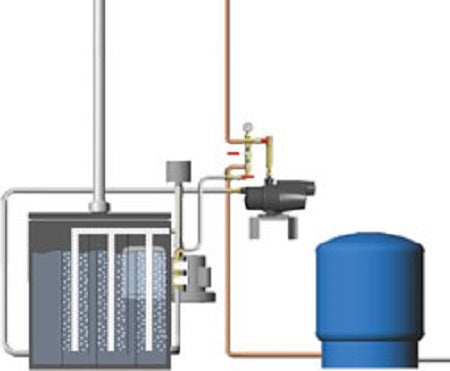
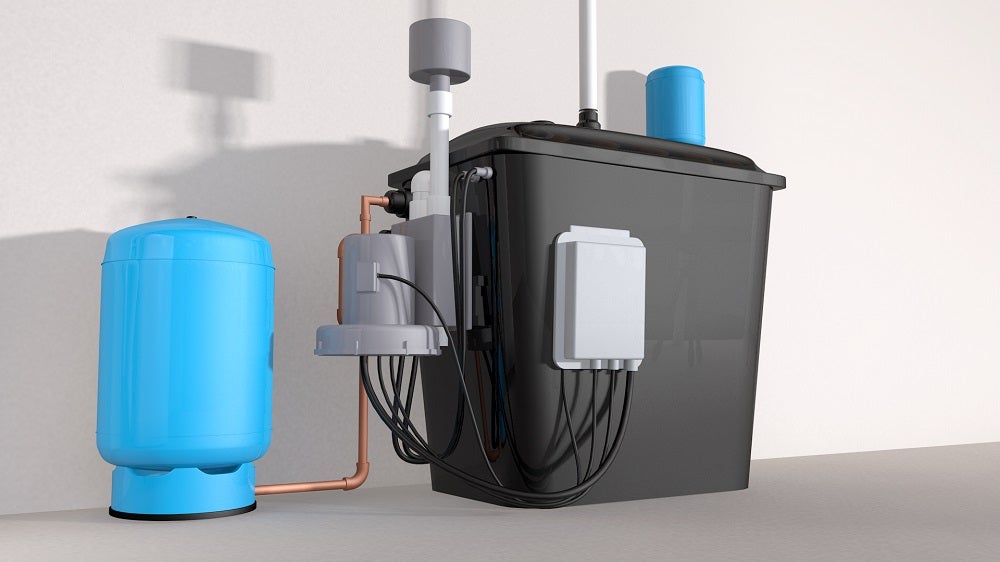
Radon Mitigation for Water
The EPA recommends a maximum contaminant level (MCL) of 4,000 picocuries per liter (pCi/L) for radon in drinking water. If radon mitigation is necessary for your water supply, contact a radon professional. They will do the following:
- Test radon levels in the water
- Check the water flow rate and determine the best radon mitigation system location, taking into consideration plumbing, electrical and venting requirements as well as your preferences.
- Offer a plan for eliminating or reducing radon levels in the water source
Aeration Systems
Aeration is the most commonly used type of radon in water reduction system. Another type is called Granular Activated Carbon (GAC). However, it’s important to know the EPA does not recommend GAC for radon levels above 5,000 pCi/L.
The aeration method is considered by the EPA to be the best technology available. It does not pose the threat of waste buildup that other methods, such as GAC, might pose. Aeration separates the radon gas from the well water, then vents the contaminants safely above the roofline.